Step-by-Step Guide to the Flex Printed Circuit Board Assembly (FPCBA) Process
Rob Larsen2025-08-21T13:12:10+00:00Introduction
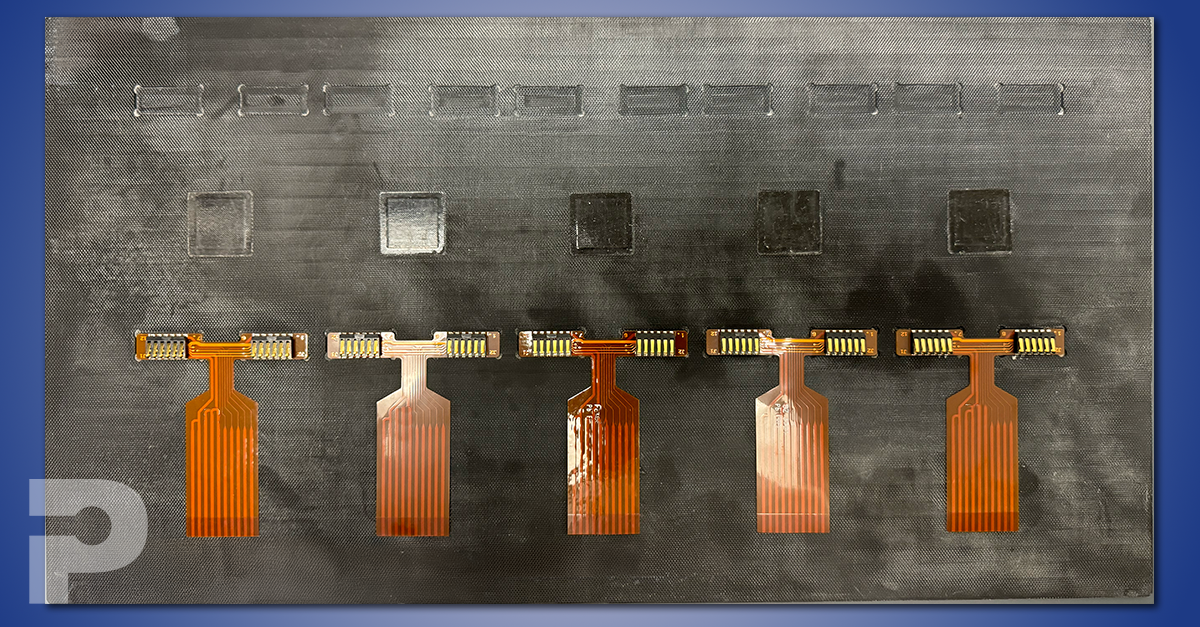
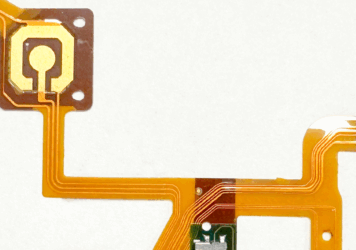
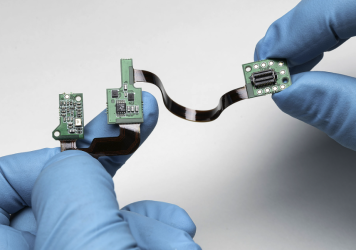
As electronics evolve to become thinner, lighter, and more complex, Flex Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs) have emerged as a key solution. But building these flexible circuits into reliable assemblies requires precision and deep expertise. In this post, we walk through the Flex Printed Circuit Board Assembly (FPCBA) process step-by-step – from handling delicate substrates to the final inspection – to help you understand what goes into high-quality flex circuit manufacturing.
1. Incoming Material Inspection
Before assembly begins, all components and bare flex PCBs undergo incoming quality control (IQC). Flex materials are more sensitive to bending, moisture, and contamination than rigid boards, so careful inspection is essential.
Checks include:
• Visual and dimensional inspection of FPCs
• Moisture sensitivity labeling and baking if required
• Component verification (value, quantity, packaging, MSL level)
2. Surface Preparation & Baking
Flex PCBs often absorb moisture, which can lead to delamination or “popcorning” during reflow. To mitigate this, boards are baked in temperature-controlled ovens to reduce moisture content.
Surface prep may also include:
• Plasma treatment for better solder adhesion
• Cleaning to remove oils or residues
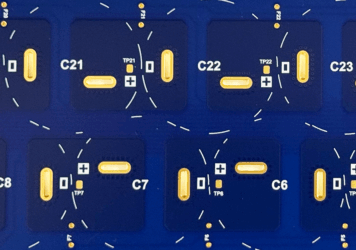
3. Stencil Printing of Solder Paste
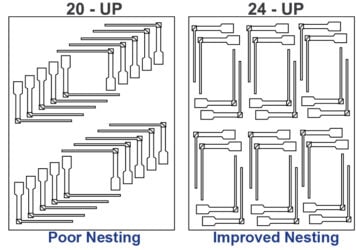
Next, a stainless-steel stencil is used to apply solder paste to the component pads on the flex circuit. Since FPCs are not rigid, they’re typically mounted to a carrier or pallet to stay flat and stable during this process.
Key factors:
• Precise alignment
• Uniform paste application
• Support tooling to prevent warping

4. Component Placement (Pick-and-Place)
Using high-speed automated machines, surface mount components (SMDs) are placed onto the solder paste deposits. Flex circuits may require custom nozzles or vision calibration to handle non-standard shapes or bends.
Considerations:
• Handling of thin or irregular substrates
• Placement accuracy for fine-pitch or small components
• Z-height and downward pressure adjustments

Ready to streamline your flex PCB assembly?
Partner with PICA for precision, reliability, and proven expertise.
5. Reflow Soldering
Reflow soldering is used to permanently attach components to the flex board. Since flex materials can’t handle high mechanical stress, the temperature profile is tightly controlled.
Critical steps:
• Gradual ramp-up to avoid thermal shock
• Controlled peak temperatures for solder melt
• Even cooling to prevent warping or cracking

6. Inspection and Cleaning
After reflow, assemblies undergo automated optical inspection (AOI) or X-ray inspection (for BGAs or dense packages). If needed, boards are cleaned to remove flux residues, which can affect long-term reliability.
Typical inspection checks:
• Solder joint integrity
• Tombstoning, bridging, or misaligned parts
• Delamination or surface defects

7. Through-Hole or Manual Assembly (if applicable)
If the flex assembly includes connectors, stiffeners, or components that require hand soldering, these are added in this step.
This may involve:
• Wave soldering (for high-volume)
• Hand soldering or selective soldering (for precise or fragile areas)

8. Stiffener Attachment & Additional Processes
To reinforce specific regions of the flex circuit (like connector areas), stiffeners or heat shields are added using adhesives or thermal bonding.
Optional post-processes include:
• Shielding film application
• Conformal coating
9. Electrical Testing
All assemblies undergo functional and continuity testing to confirm there are no open circuits or shorts.
This may include:
• Flying probe testing
• In-circuit testing (ICT)
• Custom test fixtures for FPCBA form factors

10. Final Inspection & Packaging
The final step is visual and dimensional inspection, followed by protective packaging to avoid ESD and mechanical damage.
Packaging may include:
• Anti-static bags or trays
• Custom fixtures for oddly shaped or ultra-thin assemblies
• Moisture barrier bags if required
Conclusion
Flex PCB assembly demands more than just standard SMT processes. It requires a tailored approach that respects the unique characteristics of flexible substrates and the specialized demands of lightweight, compact electronics. At PICA Manufacturing Solutions, we’ve optimized our FPCBA process to meet the high standards of industries like medical devices, automotive, and communications.
Need help with a flex circuit assembly project? Visit picamfg.com or contact us to learn how we can support your next innovation.