Blind & Buried Microvias for High-Density Interconnects
Advanced Via Structures for Compact, High-Performance PCB Design
Blind, buried, and laser-drilled microvia architectures enable ultra-dense HDI routing, allowing shorter signal paths, minimized vias stubs, cleaner impedance control, and higher I/O breakout under fine-pitch BGAs. At PICA, our HDI build-up processes combine laser drilling, copper filling, sequential lamination, and IPC-4761-compliant via protection to deliver reliable, miniaturized circuits for high-speed, RF, and harsh-environment electronics.
Why Choose Blind & Buried Microvias?
• Higher Routing Density – Increased trace channels and I/O breakouts through stacked/staggered microvias
• Optimized BGA Escape – Supports via-in-pad, fine-pitch BGAs, mmWave packages, and advanced HDI placement
• Superior Signal Integrity – Shorter interconnects reduce parasitics; copper-filled microvias eliminate voids and stubs
• Space & Cost Efficiency – Fewer layers with high-density build-up results in thinner, lighter, more economical boards
• Manufacturing Expertise – Requires advanced process controls: laser ablation, via fill, multi-core lamination, IPC-4761 conformance
Blind & Buried Microvias Capabilities – Highlights
Laser drilled microvias to 0.15 mm or smaller for layer to layer build up interconnects
Blind vias connecting surface layers to specific internal layers without deep penetration
Buried vias located completely within internal layers for advanced HDI routing
Stacked or staggered copper filled microvias for high reliability BGA via in pad structures
Sequential lamination and multi core build ups for advanced HDI density
Via in pad support using epoxy fill and copper cap plating aligned with IPC 4761 Type 7
Controlled aspect ratios that support reliable via plating quality
Reliability testing that includes X ray inspection, thermal cycling, cross sections, and 4 wire electrical verification
Global Design and Manufacturing Support
We engage early with your design team to define HDI stack ups, select appropriate via protection types, and optimize routing under BGA components. By aligning IPC requirements, consistent tolerances, and manufacturability from the start, we reduce risk across prototypes and full production.
Benefits of Blind and Buried Microvias
Ultra Dense Interconnects Made Practical
Microvias support diameters below 150 microns and reduce overall layer count by removing full depth drilling. This allows more routing area in less space while shrinking the total PCB footprint.
Superior Breakout Under BGAs
Via in pad combined with copper filling supports compact BGA escape and eliminates large fan out strategies. This is ideal for compact computing, wearables, RF modules, SOC packaging, and miniaturized electronics.
Improved Signal Path and RF Integrity
Copper filled microvias remove voids and reduce parasitic resistance and inductance. This benefit is critical for high speed SERDES, 5G mmWave devices, and RF communication performance.
Smaller Form Factor and Lower Layer Count
Buried and blind via strategies allow fewer overall layers while still increasing circuit density. This produces thinner devices with lower total cost and better functionality.
Reliable Manufacturing for Volume Production
Controlled laser drilling, resin or copper filling, lamination cycles, and IPC qualified sealing strategies provide repeatable HDI reliability across early prototypes and full scale production.
Markets We Serve with Blind and Buried Microvias
Mobile and Consumer Electronics
Miniaturized HDI designs for foldable devices, SOCs, compact RF modules, and camera subsystems.
Medical Devices
Implantable sensors, wearable monitoring platforms, and high pin count microelectronics where reliability and miniaturization are critical.
Automotive and Transportation
HDI boards in harsh vibration and thermal environments that require strong mechanical support for blind and buried vias.
Telecommunications and 5G Infrastructure
mmWave modules, routers, switching blades, and RF signal processing platforms that require clean impedance transitions.
Industrial and Defense Electronics
Satellite systems, flight computers, drones, and space restricted computing modules where rugged density is essential.

All too often Printed Circuit boards are viewed as simple two-dimensional surfaces. Nowhere is this oversimplification more evident than in the complex structure of Vias. These essential structures are critical to the form and function of any PCB with more than a single layer. Without these vias modern electronics would not be possible in the way we know them today. This paper delves into the importance of via protection, what the Institute for Printed Circuits (IPC) recommends, the types of via protection, their applications, and the inherent limitations and trade-offs.

Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) form the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing the physical platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. Among the essential elements in PCB design are vias—small holes that allow electrical connections between different layers of the board. Vias play a role in ensuring efficient routing of electrical signals, managing thermal performance, and optimizing space within complex multi-layer boards.
The blogs featured below expand on this page’s content, offering detailed insights into specific design, manufacturing, and application topics that provide added relevance and deeper context for engineers and decision-makers.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Stencil Design: Key Characteristics & Best Practices
Stencil design plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs). A well-designed stencil...
Essential Documentation for Manufacturing Bare PCBs and FPCs
When placing an order with PICA Manufacturing Solutions for bare Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) or Flexible Printed Circuits...

Essential Documentation and Data Files for PCB Component Assembly
When ordering component assembly for your Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs), it's important to...
Advanced Surface Finishes for Enhanced PCB Performance
This blog is an introduction to a white paper that contains additional information on surface finishes including: Immersion Silver or...
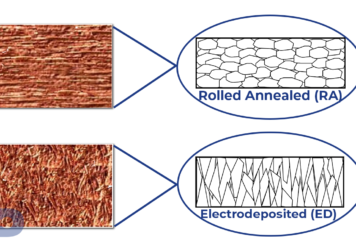
The Best Copper Conductor for Flex-to-Install & Dynamic Applications
When it comes to choosing the right conductor material for flexible printed circuits (FPC), the primary consideration revolves around...
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Via Protection: Strategies and Standards
This blog is an introduction to a larger white paper that features 7 different via protection types. Download the full white...
The Power of Embedded Passives
At PICA, we pride ourselves on being at the forefront of new technological advancements, including embedded passives. Through this blog...

6-Layer ELIC Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board / Rigid Flex PCB
A 6-Layer ELIC (Every Layer Inter-connect) Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board / Rigid Flex PCB is an advanced and...



