Navigating SMT Assembly Methods for Flexible Circuits
Simon Lim2025-07-24T15:15:15+00:00This blog is the first in a two-part series that delves into the critical factors you need to consider when deciding between panel arrays and singulated carriers for your project. In this first installment, we’ll explore the key considerations that can impact your choice and how they align with your specific needs and goals.
Part 1: Key Considerations for Choosing Between Panel Arrays and Singulated Carriers
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) component assembly on flexible circuits can be performed either on a panel array or on singulated flex circuits mounted on a carrier. As an expert in Flexible Printed Circuit Technologies, PICA Manufacturing Solutions is here to evaluate these two approaches, each of which comes with its own set of considerations, advantages, and challenges.
Before diving into these considerations and trade-offs, it’s crucial to first understand the two primary methods: Panel Array Assembly and Singulated Flex Circuit Assembly on a Carrier.
- Definitions
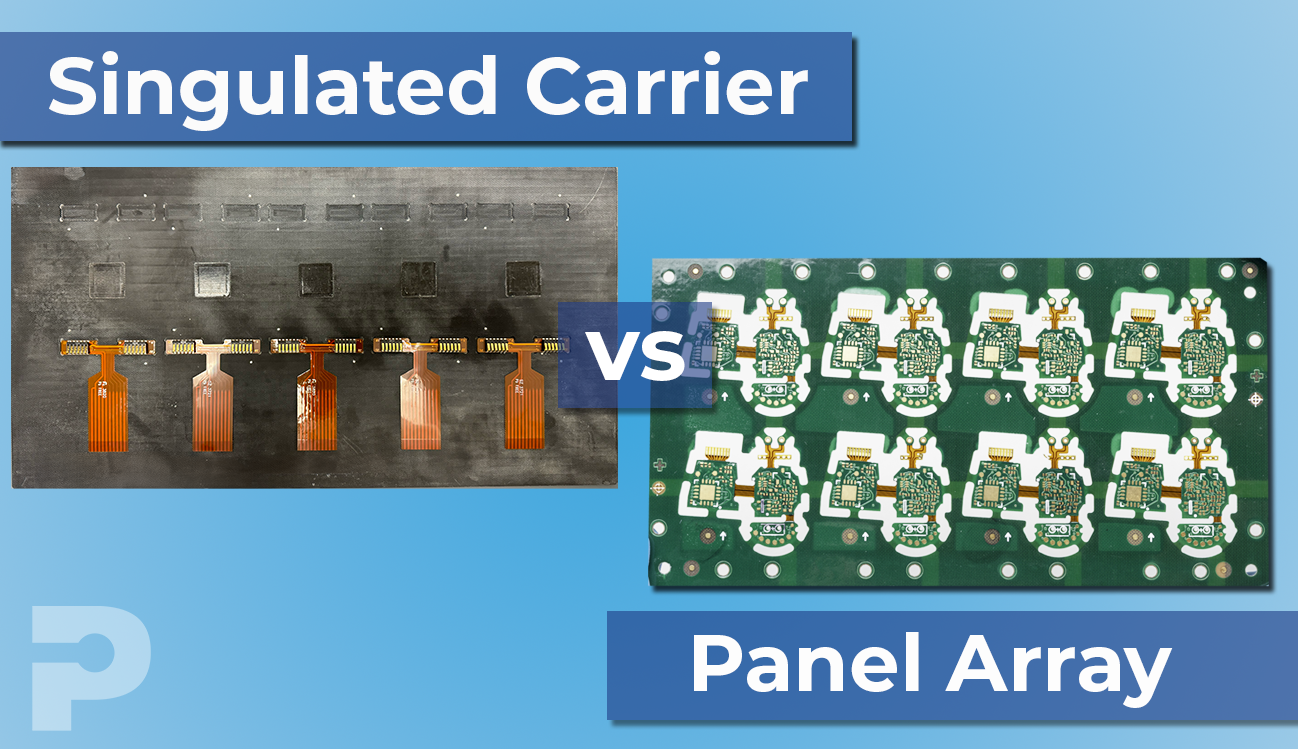
Panel Array Assembly
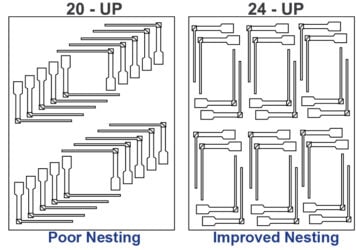
A Panel Array is a configuration where multiple flexible circuits (FPCs) are grouped together on a single, larger sheet or panel. These individual circuits are typically connected by narrow tabs or other temporary structures that hold them in place during the SMT assembly process. The entire panel is processed as a single unit during component placement, soldering, and other assembly steps. After the components have been mounted, the individual circuits are separated (singulated) from the panel, usually by breaking or cutting the connecting tabs.
Singulated Flex Circuit Assembly on a Carrier
In Singulated Flex Circuit Assembly, each flexible circuit is cut or singulated from the larger sheet before any components are mounted. These individual circuits are then placed onto a carrier, typically a rigid frame or fixture, which stabilizes them during the assembly process. The carrier holds each singulated FPC securely in place, allowing for precise component placement and soldering. After the assembly is completed, the FPCs are removed from the carrier, ready for the next stage of production or for final use.
PICA’s Capabilities
Discover the full range of capabilities and services we offer at PICA Manufacturing Solutions. Explore how our industry expertise can help you achieve your project goals with precision and efficiency.
- Considerations
Circuit Design (Size and Shape):
The complexity and shape of the flexible circuit play a crucial role in determining the assembly method. Panel arrays are often favored for simpler, more uniform designs, while singulated circuits on carriers are preferred for complex or irregular shapes.
Production Volume:
High-volume production typically benefits from the efficiency of panel arrays, where multiple circuits can be processed simultaneously. In contrast, lower volumes or custom designs may justify the additional handling required for singulated circuits on carriers.
Material Handling:
Flexible circuits, by nature, require careful handling to avoid damage. Panel arrays provide added rigidity during the assembly process, reducing the risk of warping or misalignment. However, singulated circuits mounted on carriers must be meticulously managed to maintain stability and alignment.
Production Versatility (Flexibility):
The ability to switch between different designs or production runs with minimal downtime is crucial in many manufacturing environments. Singulated circuits on carriers can offer greater flexibility in adapting to different designs or small batch production, while panel arrays are generally more efficient for consistent, high-volume production.
Component Density:
High component density can challenge the assembly process, particularly in maintaining precise alignment and avoiding solder bridging. Panel arrays typically provide better stability for high-density layouts, while singulated circuits may require additional care in alignment.
Alignment & Registration:
Ensuring accurate alignment and registration of components is critical, especially for circuits with fine-pitch components or tight tolerances. Panel arrays generally offer better control over alignment due to the rigid nature of the panel, while singulated circuits may present more challenges, especially if the carrier does not provide sufficient support.
Cost Considerations:
Cost is a crucial factor in manufacturing decisions. When evaluating the cost implications, it’s essential to assess the initial investment, maintenance, and operational costs associated with using arrays or carriers. Singulated circuits mounted on carriers can be more cost-effective, particularly in scenarios where the allowance of defective parts per panel (X-out) is a concern. X-out rates in panel arrays can drive up costs significantly, as more material and components may be wasted. In contrast, singulated circuits on carriers allow for greater control over individual circuit quality, potentially reducing overall production costs and waste.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate method for SMT component assembly on flexible circuits requires a careful assessment of multiple factors, including circuit design, production volume, material handling, production versatility, component density, alignment and registration, and cost. PICA Manufacturing Solutions is here to guide you through these considerations, ensuring that you choose the method that best suits your production goals.
In the following article, we will delve deeper into the pros and cons of both panel array assembly and singulated flex circuit assembly on a carrier, helping you make an informed decision with the expertise of PICA Manufacturing Solutions to support you every step of the way.
Contact us with any questions you have.