Impedance Control for High-Speed PCB & Flex Designs
Maintain Signal Integrity from First Trace to Final Board
In high-speed and high-frequency electronics, uncontrolled trace impedance can lead to signal reflections, data errors and compliance failures. PICA’s impedance control capabilities combine impedance modeling, stack-up design and manufacturing process control so you get accurate, repeatable impedance across your board stack-up, whether rigid, flex or rigid-flex. Our engineering team supports DDR and high-speed serial links, RF paths, differential pairs and complex mixed-signal designs from layout through production sign off.
Why Choose Impedance Control?
Reliable High-Speed Signal Integrity
Controlled impedance reduces reflections, skew and noise in GHz-level systems.Optimized Stack-Up & Materials
We tune trace width, spacing, Dk/Df values, copper weight and finish to meet target impedance.Engineer-Driven Collaboration
A design engineer reviews your rules, stack-up and impedance table to ensure manufacturability.Verified for Production
Test coupons and TDR measurement confirm that real builds match your simulations.Scalable Across Rigid & Flex
Impedance rules account for rigid, flex and rigid-flex bends, HDI routing and microvias.
Impedance Control Capabilities – Highlights
Single-ended and differential control (e.g., 50 Ω / 90–100 Ω).
Impedance modeling for microstrip, stripline and flex structures.
Stack-up definition with tuned dielectric thickness and copper geometry.
Via and return-path design for high-speed and HDI breakouts.
TDR coupon testing on production panels.
Early DFM review to align impedance goals with yield and cost.
For technical information on PICA’s Engineering expertise, click the button below.
Global Design & Manufacturing Support
We support impedance from schematic review to stack-up, layout rules and final TDR verification. U.S. engineering aligns design intent with our global manufacturing sites so impedance, lamination cycles and materials remain consistent from prototype to volume.
Benefits of Impedance Control
Mitigated Signal Integrity Risk
Uncontrolled impedance introduces reflections, ringing and eye diagram closure that degrade high-speed signals. Controlled impedance preserves rise times, timing margins and jitter performance.
Faster Time to Market
By solving impedance and stack-up questions early, you avoid last minute redesigns, failed prototypes and extended debug in the lab.
Smaller, Denser Boards
Reliable impedance control supports higher routing density, finer lines, HDI structures and dense BGA or micro-BGA packages without sacrificing signal integrity.
Reliable Across Environments
Robust impedance design helps maintain performance under thermal cycling, vibration and mechanical stress, important for automotive, industrial and aerospace applications.
Confidence in Volume Production
Defined impedance targets, stack-up drawings, coupons and TDR verification give you repeatable results and high yields when you move from pilot runs to full scale manufacturing.
Markets We Serve with Impedance Control
Digital & High-Performance Computing
Memory interfaces such as DDR and LPDDR, PCIe and other high-speed serial links, GPUs, FPGAs and advanced processors all require tight impedance control to preserve data integrity.
RF, 5G & Wireless Systems
Millimetre-wave front ends, antenna feeds, RF modules and WiFi, Bluetooth and IoT devices demand precise trace impedance and disciplined layout for low loss signal paths.
Automotive & ADAS Electronics
As data rates within vehicles increase, sensors, controllers and compute modules need impedance managed boards that maintain performance under temperature extremes and vibration.
Medical & Wearable Devices
Compact form factors, mixed-signal modules and reliable connectivity in wearable, implantable and monitoring electronics depend on controlled impedance in very small footprints.
Industrial Automation & Telecommunications
High-speed networking equipment, data centre interconnects, motor control boards and infrastructure electronics benefit from impedance verified routing and disciplined manufacturing control.
The blogs featured below expand on this page’s content, offering detailed insights into specific design, manufacturing, and application topics that provide added relevance and deeper context for engineers and decision-makers.
Designing for Precision: Controlled Impedance in Flexible Circuits
As electronic devices shrink and signal speeds increase, one design requirement becomes mission-critical: controlled impedance. This is...

Designing for HDI PCB and Fine-Line Etching: What You Need to Know
As devices shrink and performance demands grow, engineers are turning to High-Density Interconnect (HDI) technology to pack...

Why AOI and Quality Control Matter in PCB and Flex Circuit Manufacturing
Why AOI and Quality Control Matter in PCB and Flex Circuit Manufacturing When it comes to PCB and flex circuit manufacturing,...
Guide to PCB & FPC Manufacturing Processes
This blog is an excerpt from the white paper Guide to PCB & FPC Manufacturing Processes: Subtractive, Semi-Additive & Additive...
Designing High Voltage PCBs: Key Layout and Material Considerations
When working with high-voltage circuits, design priorities shift. While many PCBs focus on high-speed signaling, impedance control, or component density,...
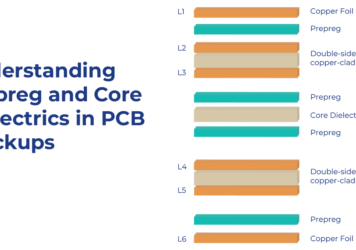
Understanding Prepreg and Core Dielectrics in PCB Stackups
In multilayer PCB fabrication, what connects copper layers together isn’t just glue—it’s carefully engineered dielectric materials that control signal...
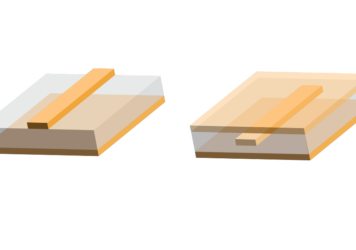
Controlled Impedance in Printed Circuit Board Design
In the design of printed circuit boards (PCBs), controlling impedance is a crucial factor for ensuring optimal signal integrity, especially...
What is Differential Impedance?
In the fast-paced realm of the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) industry, achieving optimal signal integrity is crucial for the...



