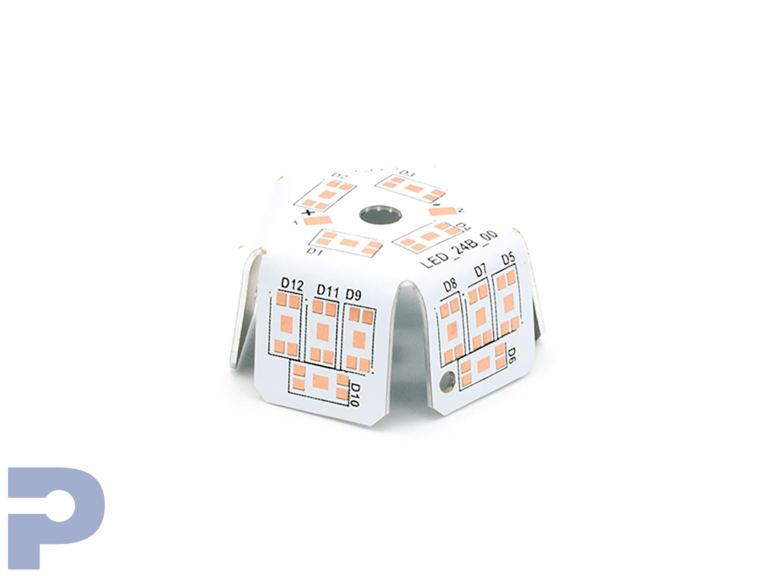
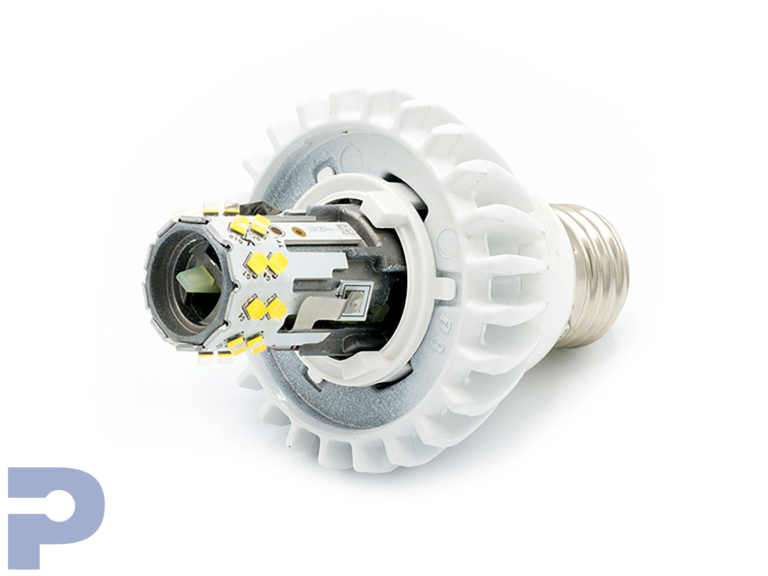
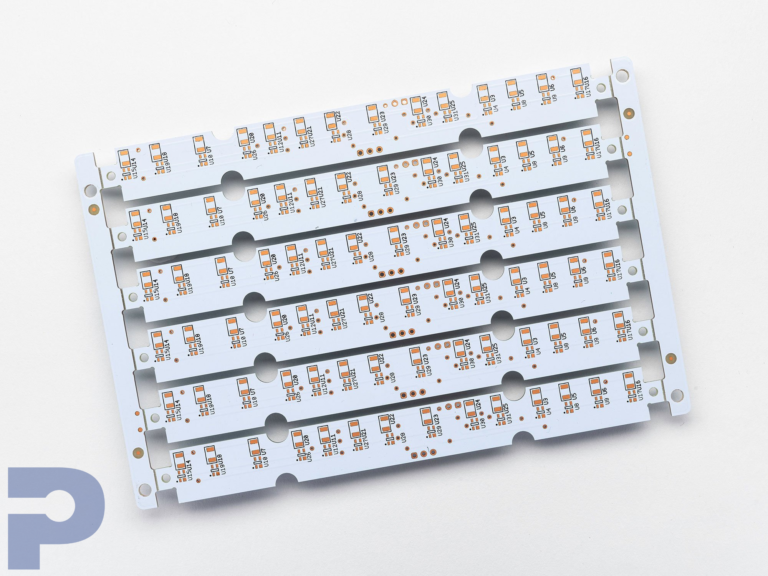
Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs)
High-Performance Thermal PCB Solutions
PICA Manufacturing Solutions specializes in Metal Core PCB manufacture, delivering high-performance MCPCBs designed for demanding thermal management applications. Built with aluminum or copper cores, our metal core boards efficiently dissipate heat away from high-power components, ensuring stability and reliability even in harsh environments.
Compared to traditional FR-4 boards, metal core PCBs provide superior heat conductivity, mechanical strength, and extended device lifespan. From single-layer to multi-layer and hybrid MCPCB assemblies, PICA delivers precision-engineered solutions tailored to your thermal, electrical, and mechanical requirements.
Why Choose PICA for Metal Core PCBs?
Thermal Expertise – Specialized in heat-dissipating PCB solutions for LED, power, and other high-temperature applications.
Engineering Support – Expert DFM guidance to optimize thermal performance, reliability, and manufacturability.
Global Manufacturing – Facilities in the U.S. and Malaysia for scalable production and responsive delivery worldwide.
Proven Reliability – Strict quality systems ensure durable, high-performance MCPCBs built for harsh environments.
Custom Solutions – Single-layer, multi-layer, and hybrid designs tailored to your electrical, thermal, and mechanical needs.
For more technical information on PICA's Metal Core PCB capabilities, click the button below.
Benefits of Metal Core PCBs
Efficient Heat Dissipation
The metal core acts as a built-in heat sink, spreading heat evenly across the board to prevent component overheating and ensure reliable operation.
Improved Reliability
By maintaining lower operating temperatures, MCPCBs reduce thermal stress, minimize solder joint fatigue, and extend the life of electronic devices.
Superior Thermal Management
With improved CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion), metal core PCBs allow for the integration of high-power components and consistent performance in demanding environments.
Markets & Applications
Medical Devices
Precise and heat-sensitive systems, where reliable thermal management is critical for performance and safety.
Automotive Electronics
Thermal solutions for rugged, vibration-prone, and high-heat automotive environments.
LED Lighting
Metal core PCBs efficiently manage heat generated by LEDs, extending lifespan and maintaining consistent light output.
Power Electronics
Ideal for power supplies, converters, and high-heat circuits requiring consistent thermal regulation.
Consumer Electronics
Used in audio amplifiers, RF modules, solar inverters, and computing hardware such as data storage systems.
Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs): Thermal Muscle for High-Power Electronics
Modern electronics pack more power into tighter spaces than ever. That heat has to go somewhere.
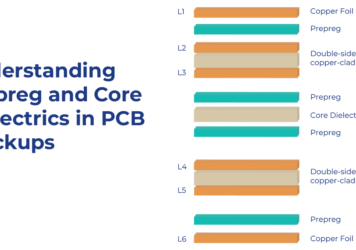
Understanding Prepreg and Core Dielectrics in PCB Stackups
In multilayer PCB fabrication, what connects copper layers together isn’t just glue—it’s carefully engineered dielectric materials that control signal...
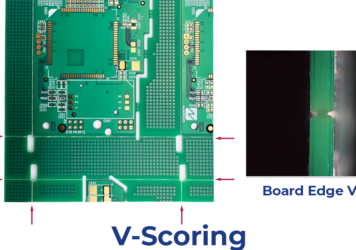
Choosing the Right PCB Separation Method: V-Scoring, Routing, and Die Cutting
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing involves precise processes, not just in design and component assembly but also in how the...

PCB Base Materials: FR-4, FR-2, CEM-1, and CEM-3
Selecting the right base material for a PCB is never a simple choice. The properties of the substrate affect everything—from...
Understanding Copper Limits & Bend Radius in Flex PCBs
Whether you're designing for a high-durability dynamic application or a compact static installation, every detail matters—from copper type and thickness...

Precision Cleaning with PICA: Ultrasonic PCB Cleaning at Our Kuala Lumpur Facility
At PICA, we know that the performance and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) depend heavily on their cleanliness....
Understanding PCB Via Holes: Through-Holes, Blind Vias, Buried Vias, & More
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) form the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing the physical platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic...
Understanding the Multi-Purpose Role of Flux in PCB Assembly
Flux is a fundamental material in the electronics manufacturing process, particularly in the assembly of printed circuit boards...
Request Your PICAKit Today
We want you to take a look at what we can produce for you by offering you a PICAKit which includes a variety of flexible pcb, shields, & flat flexible cables.