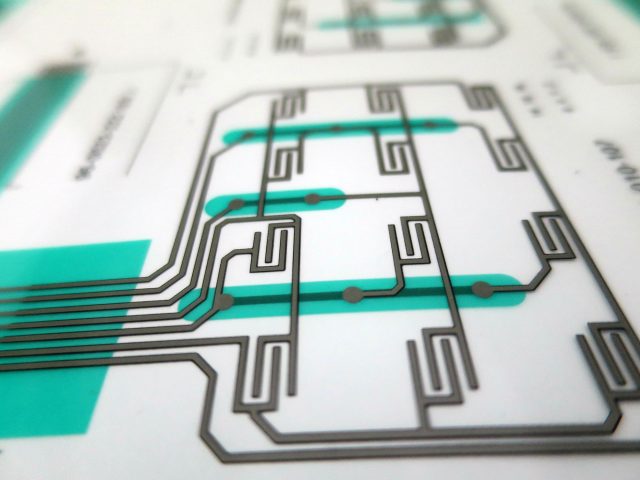
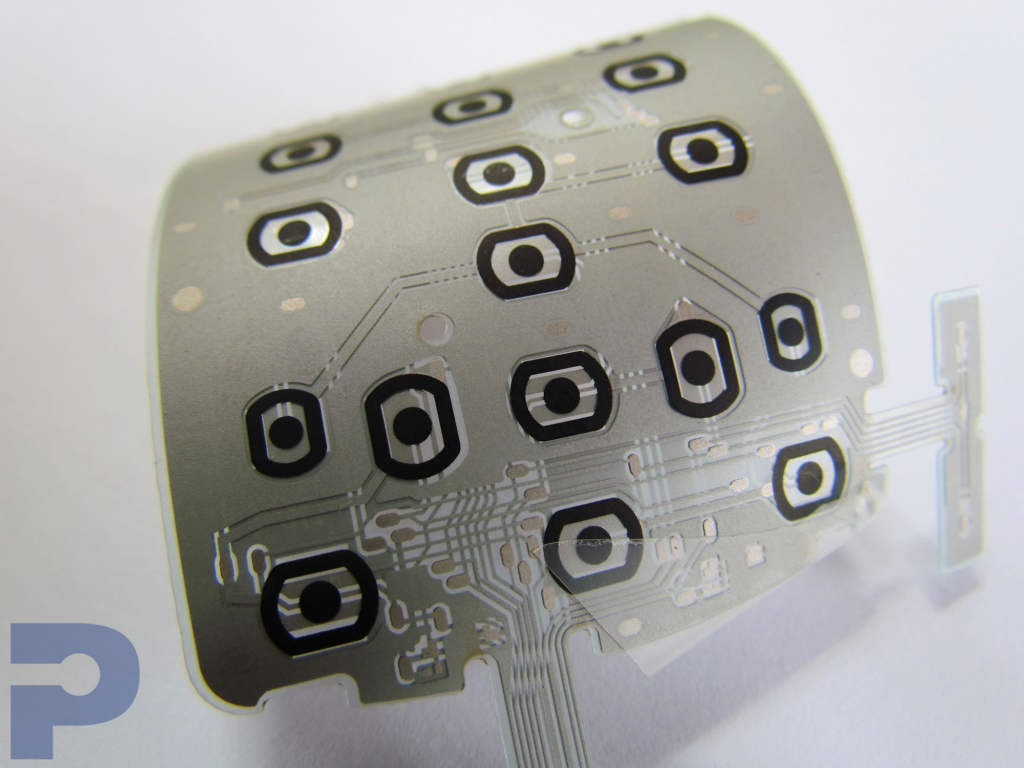
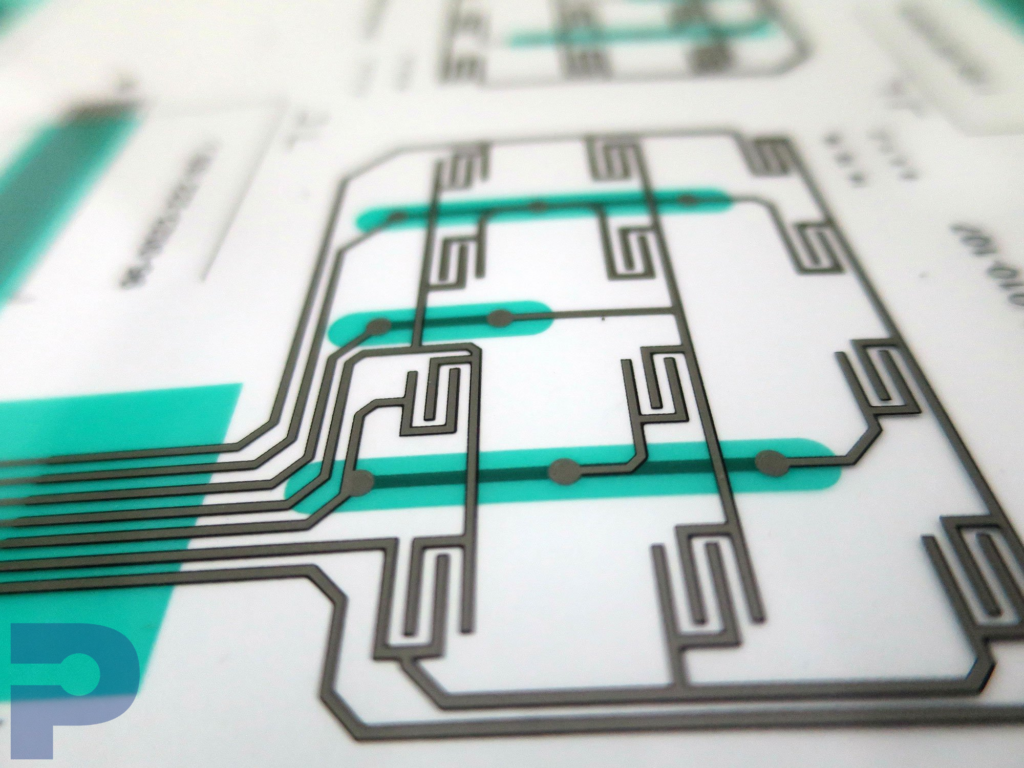
Membrane Switches
Custom Membrane Switch Assemblies for Reliable Interfaces
PICA Manufacturing Solutions designs and manufactures custom membrane switch assemblies engineered for performance, durability, and ease of integration. Built with advanced materials and precision manufacturing, our membrane switches deliver reliable user interfaces for medical devices, industrial equipment, consumer electronics, and more.
Whether you need tactile feedback, LED backlighting, custom graphic overlays, or sealed designs for harsh environments, PICA provides scalable solutions tailored to your product requirements.
Why Choose Membrane Switches?
Slim & Compact – Ultra-thin profiles save space and allow seamless integration into tight enclosures.
Durable & Reliable – Sealed construction resists moisture, dust, and wear for long-term performance.
Customizable Interfaces – Options for tactile domes, embossing, and graphic overlays create user-friendly designs.
Easy to Clean – Smooth, flat surfaces simplify sanitation, ideal for medical and industrial equipment.
Cost-Effective – Efficient materials and scalable production deliver quality interfaces at competitive costs.
Membrane Switch Capabilities – Highlights
PICA offers advanced engineering and manufacturing capabilities for membrane switches, including:
Tactile or non-tactile switch options (metal domes, polydomes, flat panels)
LED and fiber optic backlighting solutions
Graphic overlays with custom colors, logos, and icons
EMI/RFI shielding for sensitive electronic applications
Sealed designs with moisture, dust, and chemical resistance (IP-rated options)
Integration with flexible circuits or hybrid assemblies for compact system designs
Benefits
Slim Profile
Ultra-thin construction allows integration into compact devices without adding bulk.
Durable Performance
Sealed designs resist dust, moisture, and wear, extending product lifespan.
Tactile Feedback
Metal domes or polydomes provide responsive “clicks” for intuitive user interaction.
Custom Design Options
Backlighting, embossing, and graphic overlays create branded, user-friendly interfaces.
Easy Maintenance
Smooth, flat surfaces are simple to clean and sanitize, ideal for medical and industrial use.
Cost Efficiency
Efficient materials and scalable production keep interfaces affordable without sacrificing quality.
Markets We Serve with Membrane Switches
Medical Devices
Durable, easy-to-clean switches for diagnostic tools, patient monitoring, and portable devices.
Industrial Equipment
Rugged, sealed user interfaces for machinery, robotics, and control panels.
Consumer Electronics
Custom keypads and overlays for appliances, handheld devices, and wearables.
Automotive
Reliable, slim-profile switches for dashboards, interior controls, and infotainment systems.
Defense & Aerospace
Lightweight, sealed designs that withstand vibration, shock, and environmental extremes.

Conductive Inks and Their Role in Flexible and Printed Electronics
Conductive Inks and Their Role in Flexible and Printed ElectronicsAs electronics continue to evolve beyond rigid, boxy enclosures, the materials...
Understanding Copper Limits & Bend Radius in Flex PCBs
Whether you're designing for a high-durability dynamic application or a compact static installation, every detail matters—from copper type and thickness...
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Stencil Design: Key Characteristics & Best Practices
Stencil design plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs). A well-designed stencil...

Ultra-Thin Flexible Circuits: Overcoming Challenges in Dielectric Substrate
In Part 1, we explored the challenges of manufacturing ultra-thin flexible circuits with a focus on the conductive layers, highlighting...

Building Ultra-Thin Flexible Circuits: Part 1 – Conductor
One of our key customers approached PICA with the challenge of manufacturing ultra-thin flexible circuits. A critical component of this...

Adhesiveless Technologies for Flexible Circuits: Unlocking Next-Generation Performance
In the world of flexible electronics, the shift from traditional flexible copper-clad laminates (FCCLs) to adhesiveless materials represents a significant...

Compliance: Ensuring Safety and Performance in Flexible Printed Circuit Manufacturing
When developing and manufacturing flexible printed circuits (FPCs), adhering to industry standards ensures reliability, safety, and performance. Two pivotal standards...
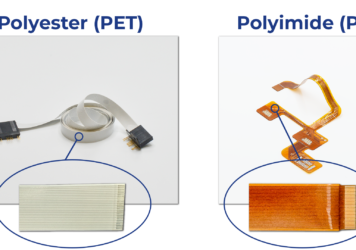
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) Dielectric Materials: Choosing the Best for Your Application
At PICA Manufacturing Solutions (PMS), we specialize in creating Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) that enable innovative designs by conforming...
Request Your PICAKit Today
We want you to take a look at what we can produce for you by offering you a PICAKit which includes a variety of flexible pcb, shields, & flat flexible cables.